Groups
Municipal Waste Treatment Plant Manufacturers
Municipal Waste Treatment Plants (MWTPs) play a pivotal role in managing and treating the ever-increasing volume of waste generated by urban populations. As cities grow and industrial activities expand, the need for efficient waste management becomes increasingly critical. MWTPs are designed to handle various types of waste, ranging from household garbage to industrial and commercial waste. This comprehensive approach is essential to safeguarding public health, protecting the environment, and promoting sustainable living. We will delve into the key aspects of Municipal Waste Treatment Plants, exploring their functions, technologies, challenges, and the importance of integrating environmentally friendly practices into waste management.
Functions of Municipal Waste Treatment Plants
Municipal Waste Treatment Plants are complex buildings that do many things to effectively handle and process waste. These are the main functions:
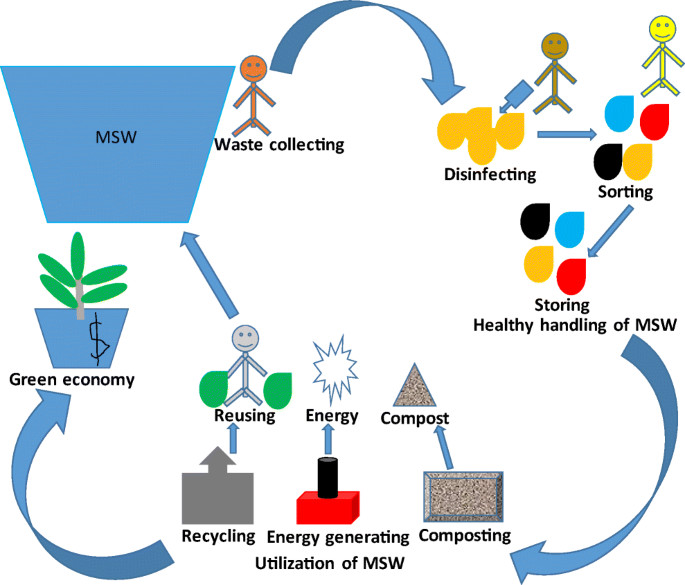
Getting waste from different places and transporting it is the first step in managing trash. This can include waste from homes, businesses, and factories. Waste collection vehicles pick up the trash and take it to the treatment plant.
Upon arrival at the treatment facility, the waste is subjected to a process of sorting and separation. This stage entails the separation of several waste categories, including recyclables, organic waste, and non-recyclables. For effective separation, sophisticated technologies are utilized, including automated sorting systems and manual labour.
Following the sorting process, the waste is treated and processed. This may encompass mechanical operations for recycling, biological treatment for organic waste, and incineration for specific waste categories. Reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills while simultaneously collecting valuable materials for recycling purposes is the objective.
Certain MWTPs integrate energy recovery mechanisms, including systems that convert waste to energy (WTE). These technologies facilitate the conversion of non-recyclable waste into usable energy, thereby contributing to the generation of renewable energy and decreasing reliance on fossil fuels.